AED 2.10
Description
The Optocoupler 817 DIP 4 EL817C is an electronic component that consists of an infrared LED and a phototransistor in a small package with four pins. It is designed to provide electrical isolation between two circuits while allowing signal transmission via light. The infrared LED emits light which is received by the phototransistor and is converted back into an electrical signal. This allows the two circuits to communicate without being physically connected, making it useful in applications where electrical isolation is necessary, such as in power supplies, motor control circuits, and audio amplifiers.
Package Includes:
- 1 x 817 DIP 4 EL817C Optocoupler IC
Features:
- Compact and easy to mount on a PCB with four pins in a DIP-4 package.
- Provides high isolation voltage of up to 5000Vrms, making it suitable for use in high voltage applications.
- Low input current of 50mA, which reduces power consumption and enables use with low-power circuits.
- A high current transfer ratio (CTR) of up to 600% ensures reliable signal transmission.
- A high collector-emitter voltage of 80V (minimum) allows for use in a wide range of applications.
- Wide operating temperature range of -55°C to +110°C, making it suitable for use in harsh environments.
Description:
The Optocoupler 817 DIP 4 EL817C, also known as an optoisolator or photocoupler, is a device that provides electrical isolation between two circuits by using light to transmit signals. It consists of an infrared LED, which emits light when an electrical current passes through it, and a phototransistor, which receives the light and converts it back into an electrical signal. The optocoupler is enclosed in a small four-pin dual inline package (DIP) that makes it easy to mount onto a printed circuit board (PCB). The pins are arranged in two rows two, with one row for the LED and the other for the phototransistor. The EL817C variant has a maximum input current of 60mA and a minimum collector-emitter voltage of 80V. The main advantage of the optocoupler is that it allows two circuits to communicate with each other without being physically connected. This is useful in situations where electrical isolation is necessary to prevent noise or voltage spikes from interfering with the signals being transmitted. Optocouplers are commonly used in power supplies, motor control circuits, and audio amplifiers, as well as in medical equipment and industrial control systems.
Principle of Work:
The EL817C optocoupler works on the principle of transmitting signals via light. It consists of an infrared LED and a phototransistor that is optically coupled, but electrically isolated from each other. When a voltage is applied to the LED, it emits light in the infrared spectrum that passes through the optically transparent material and is received by the phototransistor. The light energy is absorbed by the base-emitter junction of the phototransistor, which causes it to conduct current from the collector to the emitter. The current flowing through the phototransistor is proportional to the amount of light received from the LED, and this current can be used to drive a load or control a circuit. The EL817C optocoupler has a high current transfer ratio (CTR), which means that a small amount of input current is sufficient to switch a much larger output current. By using light to transmit signals, the EL817C optocoupler provides electrical isolation between the input and output circuits. This isolation protects the output circuit from noise and voltage spikes in the input circuit, which can cause damage or interfere with the signals being transmitted.
Pinout of the Module:
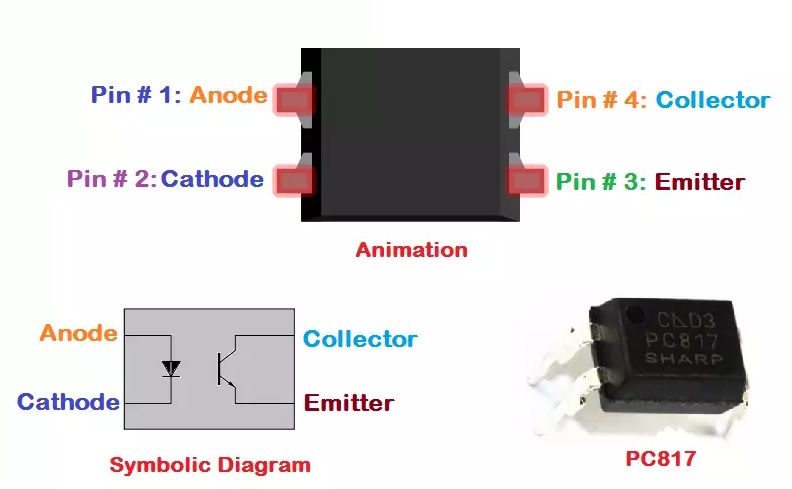
- Pin 1: Anode (+) of the infrared LED
- Pin 2: Cathode (-) of the infrared LED
- Pin 3: Emitter of the phototransistor
- Pin 4: Collector of the phototransistor
Applications:
- Power supplies: The optocoupler can be used in power supply circuits to provide feedback and control. It can also be used to isolate high-voltage and low-voltage circuits in power supplies.
- Motor control circuits: The optocoupler can be used in motor control circuits to control the speed and direction of DC motors. It can also be used to isolate the control circuit from the high-voltage motor circuit.
- Audio amplifiers: The optocoupler can be used in audio amplifiers to provide galvanic isolation between the input and output stages. This helps to reduce noise and distortion in the audio signal.
- Medical equipment: The optocoupler can be used in medical equipment to provide isolation between the patient and the medical equipment. This helps to reduce the risk of electrical shock and interference.
- Industrial control systems: The optocoupler can be used in industrial control systems to isolate and protect sensitive control circuits from noisy or high-voltage industrial equipment.
- Communication systems: The optocoupler can be used in communication systems to isolate and protect sensitive signal processing circuits from noisy or high-voltage signal sources.
- Automotive systems: The optocoupler can be used in automotive systems to isolate and protect sensitive electronic circuits from the high voltage and electromagnetic interference present in the automotive environment.
Circuit:
The scheme shows a commonly used circuit that utilizes the EL817 optocoupler integrated circuit (IC) for the purpose of driving a relay.

By connecting the anode of the optocoupler to a digital pin of a microcontroller unit, the anode can be triggered and provide current to drive a relay at the output. This circuit has various applications, such as smart switches and others.
Library:
No library needed
Code:
no code was used in the last circuit.
Technical Details:
- Isolation voltage: 5000Vrms
- Input current: 50mA (maximum)
- Reverse voltage: 6V (maximum)
- Collector-emitter voltage: 80V (minimum)
- Collector current: 50mA (maximum)
- Power dissipation: 150mW (maximum)
- Operating temperature range: -55°C to +110°C
- Package: DIP-4
Resources:
Comparison:
The EL817C and MOC3041 are both optocouplers that provide electrical isolation between input and output circuits. However, there are some differences between these two optocouplers:
- Isolation voltage: The EL817C optocoupler has a maximum isolation voltage of 5 kV, while the MOC3041 has a maximum isolation voltage of 750 V. This makes the EL817C optocoupler more suitable for applications that require higher isolation voltages.
- Output device: The EL817C optocoupler uses a phototransistor as its output device, while the MOC3041 uses a triac. The triac is capable of switching AC loads, while the phototransistor can only switch DC loads.
- Trigger current: The EL817C optocoupler has a lower trigger current (5 mA) compared to the MOC3041 (15 mA). This means that the EL817C optocoupler requires less current to turn on and can be used in circuits with lower current capacity.
- Application: The EL817C optocoupler is commonly used in power supply circuits, motor control circuits, audio amplifiers, and industrial control systems. The MOC3041 is commonly used in AC power control applications, such as lighting and motor speed control.
While both EL817C and MOC3041 are optocouplers, they have different maximum isolation voltages, output devices, trigger currents, and applications. The EL817C optocoupler is better suited for applications that require higher isolation voltages and lower trigger currents, while the MOC3041 is better suited for AC power control applications.