AED 29.50
Description
The IR Barrier Sensor E18-D80NK is a highly versatile and efficient photoelectric sensor that comprises a transmitter and a receiver. It is specifically engineered to detect objects and obstacles in a wide range of applications, making it an ideal choice for tasks such as robot obstacle avoidance, pipeline piecework, and various automation products. it has a detection distance of 3 - 80cm, This flexibility enables users to adapt the sensor's range to suit different environments and applications, ensuring optimal performance and functionality.
Package Includes:
- 1x IR Barrier Sensor E18-D80NK
Features:
- Infrared Detection: The module utilizes infrared radiation to detect the presence of objects in its surroundings.
- Modulated IR Signal: The sensor employs a modulated IR signal to ensure reliable and accurate detection while mitigating interference caused by ambient light sources, such as light bulbs or sunlight.
- Detection Range: The module provides an obstacle detection range of 3 cm to 80 cm, allowing for flexibility in proximity sensing applications.
- Advanced Sensing Capabilities: The sensor is capable of sensing not only the presence of objects but also detecting motion and measuring the amount of heat released by an object.
- Low Cost: The module offers advanced functionality at an affordable price, making it a cost-effective choice for various projects and applications.
- Compact Size: The sensor has a compact form factor, making it easy to integrate into different systems and installations.
- Easy Interfacing: The module can be easily interfaced with microcontrollers, such as Arduino, for seamless integration into projects and systems.
- Wide Application Range: The sensor is suitable for a wide range of applications, including intruder alarms, light switches, home automation, industrial automation, and more.
- Reliable Performance: With its modulated IR signal and effective interference rejection, the module ensures consistent and reliable performance in diverse environments and lighting conditions.
- User-Friendly Operation: The module is designed for easy operation and integration, offering a user-friendly experience for both beginners and experienced users.
- Durable Construction: The module is built with sturdy materials, ensuring durability and long-lasting performance.
- Low Power Consumption: The sensor has low power consumption, making it suitable for battery-powered or energy-efficient applications.
Description:
The E18-D80NK IR Proximity Sensor is an advanced and cost-effective solution for detecting the physical presence of objects in its surroundings. Utilizing infrared radiation, this electronic module can emit and/or detect infrared waves to accomplish its sensing tasks. In addition to detecting objects, the IR sensor is capable of sensing motion and measuring the amount of heat released by an object. IR sensors are widely utilized in various applications, including intruder alarms, light switches, and both home and industrial automation systems. However, it's important to note that traditional IR sensors encounter limitations when exposed to sunlight. This is because the sun emits its own infrared waves, leading to potential interference with the sensor's readings. To mitigate this issue, a common solution is to modulate the IR signal. By implementing modulation, the IR sensor becomes capable of detecting variations in the IR signal rather than relying on a fixed IR level. This modulation protects the sensor from disturbances caused by ambient light sources like light bulbs or sunlight, ensuring accurate and reliable detection in challenging environments. The E18-D80NK IR Proximity Sensor is specifically designed to address these challenges. It offers advanced features and functionality at a low cost, making it an attractive choice for a wide range of projects. With an obstacle detection range spanning from 3 cm to 80 cm, this sensor provides a flexible and adjustable detection capability to suit various proximity sensing requirements. By incorporating modulated IR signals, the E18-D80NK sensor is shielded from interferences caused by the normal light emitted by light bulbs or sunlight. This ensures consistent and accurate readings, even in environments with high-light exposure. As a result, the E18-D80NK enables precise and reliable obstacle detection in diverse scenarios, making it an excellent choice for applications requiring proximity sensing capabilities.
Principle of Work:
The E18-D80NK IR Proximity Sensor operates based on the principles of infrared reflection and reception. The sensor consists of a transmitter and a receiver, which work together to detect the presence of objects and obstacles.
- Transmitter: The transmitter component emits infrared radiation in the form of an IR beam or signal. This IR signal is modulated, meaning it is varied in a specific pattern or frequency. Modulation helps distinguish the transmitted signal from ambient light sources and reduces interference.
- Receiver: The receiver component is responsible for receiving the modulated IR signal after it interacts with objects in its detection range. The receiver typically consists of a photodiode or a phototransistor that converts the received infrared radiation into an electrical signal.
The internal working of the sensor can be summarized in the following steps:
- IR Emission: The transmitter emits a modulated IR signal, typically in the near-infrared spectrum.
- Signal Reflection: When the emitted IR signal encounters an object or obstacle within the sensor's detection range, some of the IR radiation is reflected or scattered.
- Signal Reception: The receiver component captures the reflected IR signal. The photodiode or phototransistor in the receiver converts the received IR radiation into an electrical signal.
- Signal Processing: The electrical signal from the receiver is then processed to determine the presence or absence of objects. The processing circuitry may involve amplification, filtering, and demodulation to extract the relevant information from the received signal.
- Output Signal: Based on the processed signal, the sensor generates an output indicating the detection of an object or obstacle. This output can be in the form of a digital signal (e.g., HIGH or LOW) or an analog signal (e.g., voltage level) depending on the specific sensor model and configuration.
- Distance Calculation: Some IR proximity sensors, including the E18-D80NK, use the strength of the received signal to estimate the distance between the sensor and the detected object. By analyzing the received signal's intensity or time of flight, the sensor can approximate the distance to the object within its specified detection range.
Pinout of the Sensor:
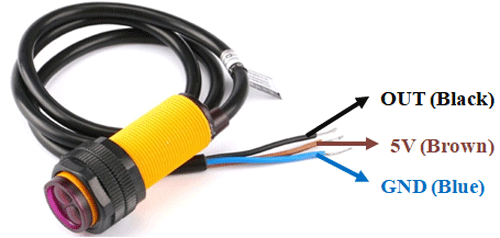
- VCC: This pin is used to supply power to the sensor. It is connected to a regulated +5V DC power source.
- GND: This pin is the ground or common reference for the sensor. It is connected to the ground or 0V of the power supply.
- OUT: This pin is the output pin of the sensor. It provides a signal that indicates the presence or absence of an object within the sensor's detection range. The output can be in the form of a digital signal, such as HIGH or LOW, or an analog signal, such as a varying voltage level.
Applications:
- Robot Obstacle Avoidance: The sensor is widely used in robotics to detect objects and obstacles, allowing robots to navigate their environment safely and avoid collisions.
- Automation Systems: The sensor can be employed in industrial automation systems to detect the presence of objects on conveyor belts, assembly lines, or robotic arms. It enables precise control and automation of processes.
- Security Systems: The sensor is used in intruder alarm systems to detect the presence of individuals or unauthorized objects in restricted areas.
- Proximity Switches: The sensor can function as a proximity switch for various applications, such as activating or deactivating lighting systems, opening doors, or triggering other electronic devices based on the proximity of objects.
- Liquid Level Detection: The sensor can be utilized to detect the level of liquids in tanks or containers. It provides a non-contact method for liquid level monitoring.
- Home Automation: The sensor is employed in home automation systems for functions such as automatic door opening, occupancy detection for lighting control, and proximity-based triggering of appliances.
- Object Detection in Vending Machines: The sensor can be used in vending machines to detect the presence of products and ensure proper delivery.
- Gaming and Interactive Systems: The sensor can be incorporated into gaming or interactive systems to detect player movements or gestures for control and interaction purposes.
- Traffic Monitoring: The sensor can be applied in traffic monitoring systems to detect the presence of vehicles at intersections, triggering traffic signal changes based on traffic flow.
- Industrial Safety: The sensor can contribute to industrial safety systems by detecting the presence of personnel in hazardous areas and triggering safety protocols or machinery shutdowns.
Circuit:
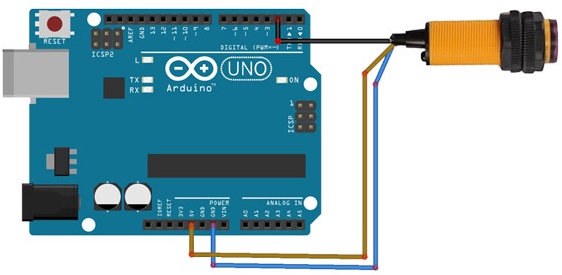
To connect the E18-D80NK IR Proximity Sensor to an Arduino Uno:
- Connect the VCC (power) pin of the sensor to the 5V pin on the Arduino Uno.
- Connect the GND (ground) pin of the sensor to the GND pin on the Arduino Uno.
- Connect the OUT (output) pin of the sensor to pin 2 on the Arduino Uno.
This setup ensures that the sensor is properly powered and allows the Arduino to read the sensor's output on pin 2.
Library:
This Module doesn't need any Library to function.
Code:
A sample code that demonstrates how to read the output of the E18-D80NK IR Proximity Sensor connected to pin 2 of an Arduino board and outputting the status of the sensor using the serial monitor:
// Define the sensor output pin
const int sensorPin = 2;
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication for debugging
Serial.begin(9600);
// Set the sensor pin as input
pinMode(sensorPin, INPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Read the sensor output
int sensorValue = digitalRead(sensorPin);
// Print the sensor value (HIGH or LOW) to the serial monitor
Serial.print("Sensor value: ");
Serial.println(sensorValue);
// Add a small delay between readings
delay(100);
}
- Make sure you have the Arduino connected to your computer, and open the Serial Monitor in the Arduino IDE (set the baud rate to 9600) to observe the sensor readings.
- In this code, we define
sensorPinas the pin number to which the sensor output is connected (in this case, pin 2). In thesetup()function, we initialize the serial communication for debugging purposes and set the sensor pin as an input. In theloop()function, we read the sensor output usingdigitalRead(sensorPin)and store the value in thesensorValuevariable. We then print the value to the serial monitor usingSerial.print()andSerial.println()for display. Finally, we introduce a small delay of 100 milliseconds usingdelay(100)between each sensor reading. - Upload the code to your Arduino board, and you should see the sensor readings (either HIGH or LOW) displayed in the Serial Monitor as the sensor detects objects or obstacles within its range.
Technical Details:
- Input Voltage: 5V
- Current Consumption: 25-100 mA
- Response time <2ms
- Sensor type: Diffuse reflective type
- Sensing range: 3-80 cm
- Cable length: 45 cm
Resources:
Comparisons:
The E18-D80NK sensor and the GP2Y0A02YK0F sensor are both commonly used in proximity sensing and object detection applications. But still, there are some notable differences between the two sensors:
- Detection Range: The E18-D80NK sensor has an adjustable obstacle detection range of 3 cm to 80 cm. In contrast, the GP2Y0A02YK0F sensor has a longer fixed detection range of 20 cm to 150 cm. This means that the GP2Y0A02YK0F sensor can detect objects at a greater distance compared to the E18-D80NK.
- Sensing Technology: The E18-D80NK sensor utilizes infrared (IR) reflection for object detection, while the GP2Y0A02YK0F sensor uses infrared (IR) distance measurement technology based on the triangulation principle. This difference in sensing technology can impact factors such as accuracy, response time, and susceptibility to environmental conditions.
- Output Type: The E18-D80NK sensor typically provides a digital output (HIGH or LOW) or an analog output (voltage level) to indicate the presence of an object. On the other hand, the GP2Y0A02YK0F sensor provides an analog output voltage that corresponds to the measured distance.
- Power Requirements: Both sensors can operate with a 5V power supply commonly used with Arduino boards. However, the specific power consumption and electrical characteristics may differ between the two sensors. It's important to refer to the datasheets of each sensor for detailed specifications.
- Application Suitability: Due to their different detection ranges and sensing technologies, the sensors may be more suitable for specific applications. For example, the E18-D80NK sensor with its adjustable range might be better suited for close-range detection and obstacle avoidance in robotics, while the GP2Y0A02YK0F sensor's longer detection range could be advantageous for distance measurement in applications such as industrial automation or object tracking.