AED 4.20
Description
The IRFZ44NPBF is an N-channel MOSFET used for power applications, designed to handle high current loads and high voltage levels. It is commonly used in motor control, power supplies, and switching circuits, and has a maximum drain-source voltage of 55V, a continuous drain current of 49A, and a low on-state resistance of 17mΩ. The TO220 packaging allows for easy mounting on a heatsink for efficient heat dissipation.
Package Includes:
- 1 x IRFZ44NPBF N-channel MOSFET
Features:
- High power handling capability, suitable for a wide range of power applications.
- Low gate charge for fast and efficient switching.
- Fast switching speed and low switching loss, leading to higher efficiency and lower power dissipation.
- Robust design for high reliability and longer lifespan.
- Easy to use and integrate into electronic circuits due to its standard TO220 package.
- Can be used as a high-power switch or as a variable resistance component.
- Low input capacitance for improved noise immunity.
- Able to operate in high-temperature environments with appropriate cooling.
- Low output capacitance for better switching performance.
- High avalanche ruggedness, meaning it can withstand high-energy pulses without damage.
Description:
The IRFZ44NPBF is a specific type of N-channel MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor) designed for power applications. MOSFETs are commonly used as switches and amplifiers in electronic circuits, and the IRFZ44NPBF is specifically designed to handle high current loads and high voltage levels. The "N-channel" designation indicates that the MOSFET is designed with an N-type channel between the source and drain terminals, which allows for the flow of electrons (or negative charge carriers) from source to drain. This is in contrast to P-channel MOSFETs, which have a P-type channel and allow for the flow of positively charged carriers (holes) from source to drain. The IRFZ44NPBF is designed to be used in applications that require high-power handling, such as motor control, power supplies, and switching circuits. Its TO220 packaging allows for easy mounting on a heatsink for efficient heat dissipation. Some of the key specifications of the IRFZ44NPBF include a maximum drain-source voltage of 55V, a continuous drain current of 49A, and a low on-state resistance of 17mΩ, which allows for efficient power handling and minimal power loss.
Principle of Work:
The IRFZ44NPBF is a power MOSFET that operates based on the principle of Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (MOSFET) technology. MOSFETs are widely used in power electronics applications because they are able to switch high voltage and high current loads with very low power consumption and heat dissipation.
The IRFZ44NPBF MOSFET consists of three terminals: the Gate (G), the Drain (D), and the Source (S). The MOSFET works by controlling the current flow between the Drain and Source terminals using an electric field created by the voltage applied to the Gate terminal. When a voltage is applied to the Gate terminal, it creates an electric field that attracts the free electrons in the N-channel towards the oxide layer. This field effectively creates a channel between the Drain and Source terminals, allowing current to flow through the MOSFET. The IRFZ44NPBF MOSFET is an N-channel MOSFET, which means that the N-type semiconductor material is used as the channel. The N-channel MOSFET is turned on when a positive voltage is applied to the Gate terminal, allowing electrons to flow from the Drain to the Source.
The MOSFET is turned off when the voltage on the Gate terminal is zero or negative, which creates a depletion region and blocks the flow of current between the Drain and Source terminals. This makes the MOSFET an ideal choice for use in applications such as power supplies, motor control circuits, and switching circuits, where high efficiency and low power dissipation are important.
Pinout:
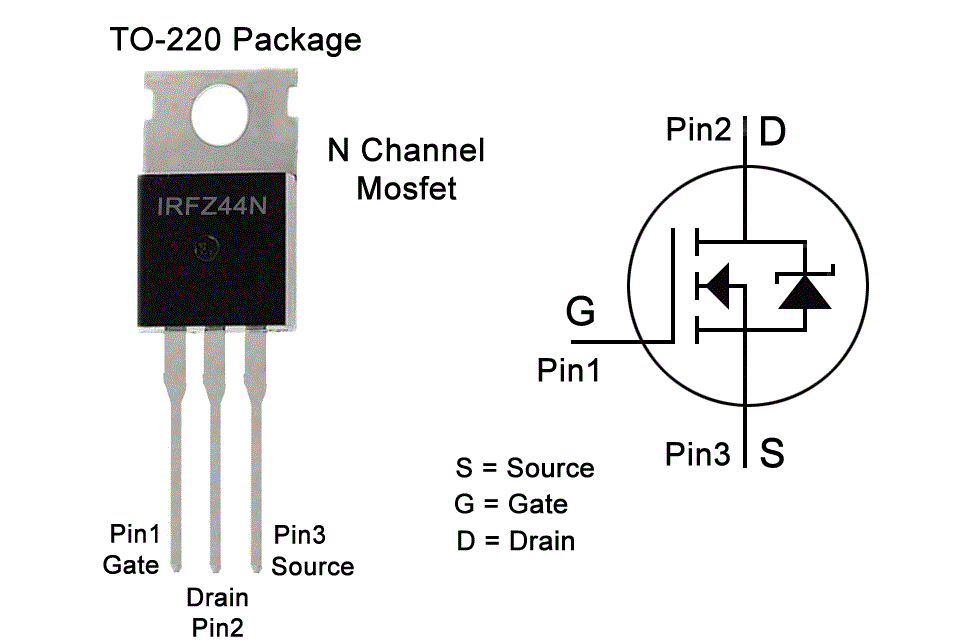
- Gate (G) - controls the current flow between the Drain and Source terminals by varying the electric field created by the voltage applied to the Gate terminal.
- Drain (D) - serves as the output terminal for the current flowing through the MOSFET to the load.
- Source (S) - serves as the input terminal for the current flowing through the MOSFET from the source.
-
The pinout sequence is: G (Gate), D (Drain), S (Source).
Applications:
- Switching power supplies: The IRFZ44NPBF is used in high-efficiency switching power supplies to convert the input DC voltage to the required output voltage.
- Motor control: The IRFZ44NPBF can be used to control the speed of DC motors by varying the voltage and current.
- Lighting control: The MOSFET can be used in lighting control circuits to control the brightness of light-emitting diodes (LEDs).
- Audio amplifiers: The MOSFET can be used in audio amplifiers to provide high power amplification of audio signals.
- Inverters: The IRFZ44NPBF can be used in inverter circuits to convert DC voltage to AC voltage.
- Battery charging circuits: The MOSFET is used in battery charging circuits to regulate the charging current and voltage to the battery.
- High current switch: The IRFZ44NPBF can be used as a high current switch in power electronics applications.
Circuit:
Using the IRFZ44NPBF MOSFET as a switch to control a DC motor or any small load are as follows:
Components:
- IRFZ44NPBF MOSFET
- DC motor 6-36v
- 6-35V battery
- 10K ohm resistor
- Push button switch
Circuit connections:
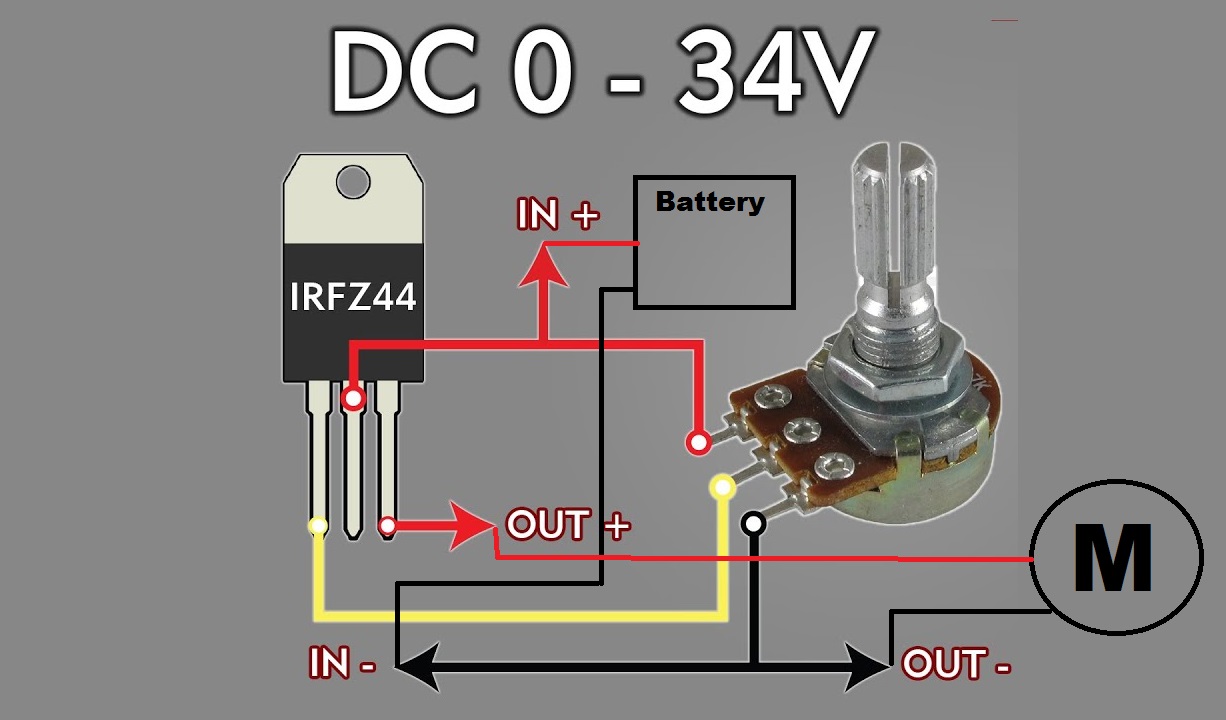
- Connect the Drain pin of the MOSFET to the negative terminal of the motor.
- Connect the positive terminal of the motor to the positive terminal of the battery.
- Connect the Source pin of the MOSFET to the negative terminal of the battery.
- Connect the Gate pin of the MOSFET to one of the pins of the push button switch.
- Connect the other pin of the push button switch to the positive terminal of the 9V battery.
- Connect a 10K ohm resistor between tas you see in the circuit scheme
Library:
we used no code in this application
Code:
we used no code in this application
Technical Details:
- VDS (Drain-to-Source Voltage): 55V
- VGS (Gate-to-Source Voltage): ±20V
- ID (Continuous Drain Current): 49A
- IDM (Pulsed Drain Current): 196A
- RDS(on) (Static Drain-to-Source On-Resistance): 17.5mΩ
- Qg (Gate Charge): 60nC
- Package Type: TO-220AB
- Operating Temperature Range: -55°C to 175°C
Resources:
Comparisons:
The IRFZ44NPBF and TIP120 are both power transistors used in electronic circuits. However, they have some differences in terms of their specifications and applications. Here's a brief comparison between the two:
- Technology: The IRFZ44NPBF is a MOSFET, while the TIP120 is a Darlington transistor.
- Voltage rating: The IRFZ44NPBF has a maximum voltage rating of 55V, while the TIP120 has a maximum voltage rating of 60V.
- Current rating: The IRFZ44NPBF has a continuous drain current rating of 49A and a pulsed drain current rating of 196A, while the TIP120 has a maximum collector current rating of 5A.
- On-resistance: The IRFZ44NPBF has a static drain-to-source on-resistance of 17.5mΩ, which is lower than the TIP120's collector-emitter saturation voltage of about 2V.
- Switching speed: The IRFZ44NPBF has a faster switching speed than the TIP120, which means it can switch on and off more quickly and efficiently.
- Cost: The TIP120 is generally less expensive than the IRFZ44NPBF.
In terms of applications, the IRFZ44NPBF is commonly used in high-power switching applications, such as motor control, power supplies, and inverters, where fast switching and high current capability are required. The TIP120 is often used in lower-power applications, such as small signal amplification and driving small motors.